题目 Title
Drag and lift forces on bed sediments in open-channel flow through boulders at various Froude numbers
期刊 Journal
Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface (IF=3.8)
作者 Author
Tang, Z. D.; Stoesser, T.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Fang, H. W.
摘要 Abstract
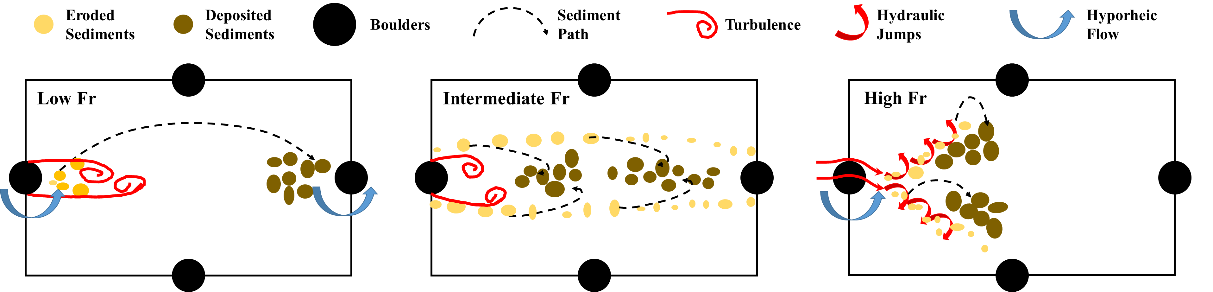
The Froude number (Fr) is an important parameter that affects turbulence structures, bedload transport, and bedforms in mountain rivers. In a prior study by Liu et al. (2024, https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0222673), turbulence structures in open channel flow through a boulder array placed on seven layers of spheres (comprising the channel bed), with Fr ranging from 0.15 to 0.89, have been quantified. This paper investigates the drag (Fx) and lift (Fz) forces on the spheres of the top layer of the bed surrounding the boulders and their response to the boulder-induced turbulence and hyporheic flow. The time-averaged drag and lift forces (Fx and Fz) in the vicinity of boulders reach up to 6 and 4 times the reach-averaged shear force (Fsph), respectively, and their standard deviations are even higher, being 2.9 or 4.4 times the time-averaged forces, respectively. Consequently, maximum instantaneous forces on the surrounding bed spheres can approach values of an order of magnitude greater than Fsph. The pre-multiplied spectra of force fluctuations, which decompose the total fluctuations into components of different length scales, reveal three predominant contributions: (a) a 1.6D length-scale contribution at high Fr, (b) a 2.1D length-scale contribution at low and intermediate Fr, and (c) a 4.5D length-sale contribution at low and high Fr, where D is the boulder diameter. These correspond to elongated rollers, oscillating boulder wakes, and hyporheic flow, respectively. Cross-correlations between force and velocity fluctuations indicate that forces on the bed spheres in boulder wakes are governed by hyporheic flow at low and high Fr, and by vortex shedding at intermediate Fr. The contributions from hyporheic flow to total drag and lift force fluctuations are highest at high Fr, reaching up to approximately 30% and 50% locally, respectively. Finally, regions of sediment deposition are predicted based on three types of criteria: near-wall shear stress, time-averaged forces, and instantaneous forces, among which regions based on the instantaneous forces align remarkably well with the deposition patterns observed by Papanicolaou et al. (2018, https://doi.org/10.1029/2018jf004753) for different Fr.
简介 Brief introduction
本文研究了围绕石块的河床最上层球体所受的阻力(Fx)和升力(Fz),以及它们对石块引起的湍流和浅层水流的响应。石块周围区域附近的时间平均阻力和升力(Fx和 Fz)分别达到平均流体剪切力(Fsph)的 6 倍和 4 倍,其标准偏差甚至更高,分别为平均力的 2.9 倍和 4.4 倍。因此,周围河床球体所受的最大瞬时力可接近Fsph值的一个数量级更大值。力波动的预乘谱将总波动分解为不同长度尺度的组成部分,揭示了三个主要贡献:(a)在高 Fr 时存在一个 1.6D 长度尺度的贡献;(b)在低和中等 Fr 时存在一个 2.1D 长度尺度的贡献;(c)在低和高 Fr 时存在一个 4.5D 长度尺度的贡献,其中 D 是巨石的直径。这些分别对应于拉长的滚石、振荡的巨石尾流以及潜流。力和速度波动之间的互相关表明,在巨石尾流中的床面球体上的力在低和高 Fr 时受潜流的控制,在中等 Fr 时受涡旋脱落的影响。潜流对总阻力和升力波动的贡献在高 Fr 时最高,局部范围内分别达到约 30%和 50%。最后,根据三种类型的标准预测了沉积区域:近壁剪切应力、时间平均力和瞬时力。其中基于瞬时力的区域与Papanicolaou等人(2018 年,https://doi.org/10.1029/2018jf004753)针对不同 Fr 值所观察到的沉积模式高度吻合。
扫码关注立方体公众号,实时追踪课题组最新科研进展



