题目 Title
Transport Mechanisms of Conservative Contaminants From Tidally Influenced Semi-Confined Aquifers to the Sea
期刊 Journal
Geophysical Research Letters (IF=5.2)
作者 Author
Zhang, J. X.; Lu, C. H.; Fang, H. W.; Luo, J.; Michael, H. A.; Wilson, A. M.
摘要 Abstract
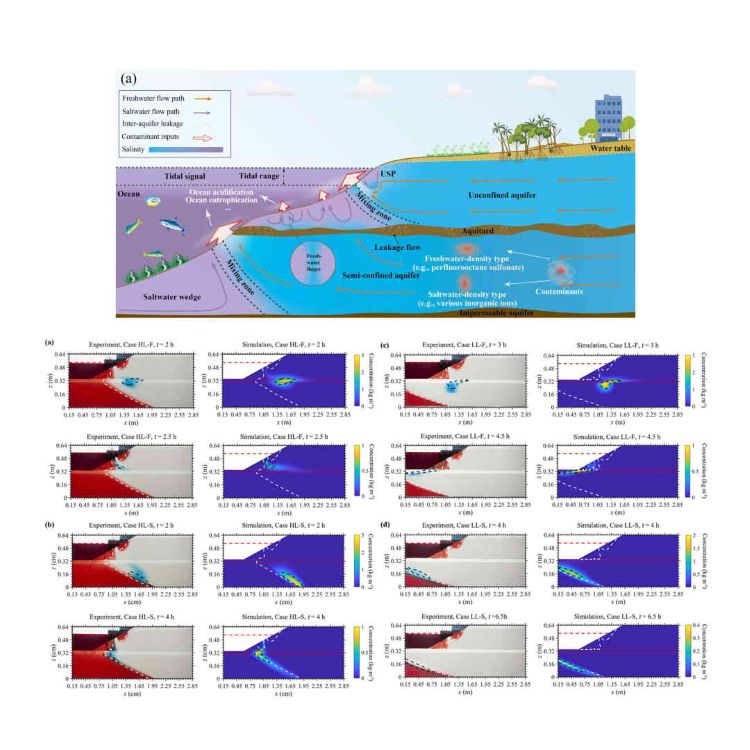
Groundwater contamination in confined aquifers is an increasingly critical issue, yet the dynamic processes governing contaminant transport between semi-confined aquifers and the ocean remain insufficiently understood. This study explores these processes within semi-confined aquifers using laboratory experiments and numerical simulations. The results reveal, for the first time, that contaminants from semi-confined aquifers mix within the interiors of overlying saltwater wedges in unconfined aquifers. As aquitard permeability decreases, contaminant composition mixed within overlying wedges changes from saltwater-density to freshwater-density counterparts. Two primary retention mechanisms are identified for deep-layer contaminants: One involves entrapment within aquitards, facilitating the mixing of contaminants into overlying wedges; the other arises from gravity-induced mixing between saltwater-density plumes and saltwater wedges. Interestingly, the residence times of freshwater-density and saltwater-density contaminants increase initially and then decline with reduced aquitard permeability. These findings enhance our understanding of the complex processes involved in deep-layer contaminant transport and retention in coastal aquifers.
简介 Brief introduction
深井污水排放、化石能源开采以及废弃水井渗漏将大量污染物引入半承压含水层系统,导致深层地下水的污染问题日益严峻。然而,关于陆源污染物从半承压含水层向海洋排泄的动力学过程仍缺乏足够的认识。为此,本研究采用室内试验和数值模拟相结合的研究方法,探究了保守性陆源溶质从半承压含水层传输到海洋的动力学行为。研究结果首次发现了深层污染物与上覆盐水楔内部盐水的混合,表明部分深层污染物会越迁至潜水含水层后再排入海洋。随隔水层的渗透系数降低,混入上覆盐水楔的污染物从盐水密度型(即变密度流体)转变为淡水密度型(即常密度流体)。研究结果进一步揭示了深层污染物两种主要的滞留机理:一是在隔水层中的阻滞作用,促使污染物混入上覆盐水楔;二是盐水密度羽流和盐水楔之间在重力驱动下的混合作用。当隔水层渗透系数减小时,污染物滞留时间增长至峰值后转为衰减,该现象证实隔水层渗透系数与深层污染物滞留时长之间存在非单调响应关系。本研究揭示的溶质运移规律为滨海深层含水层系统中污染物迁移的动力学机制解析提供了新的理论视角,为该地区地下水资源保护与水污染防治提供了重要的理论基础。
扫码关注立方体公众号,实时追踪课题组最新科研进展



