题目 Title
Toward mitigating the impact of non-bulk defects on describing water structure in salt aqueous solutions: Characterizing solution density with a network-based structural indicator
期刊 Journal
The Journal of Chemical Physics (IF=3.6)
作者 Author
Han, J. L.; Gao, Y. T.; Feng, Y. X.; Yu, Z. W.; Wu, J.; Fang, H. W.
摘要 Abstract
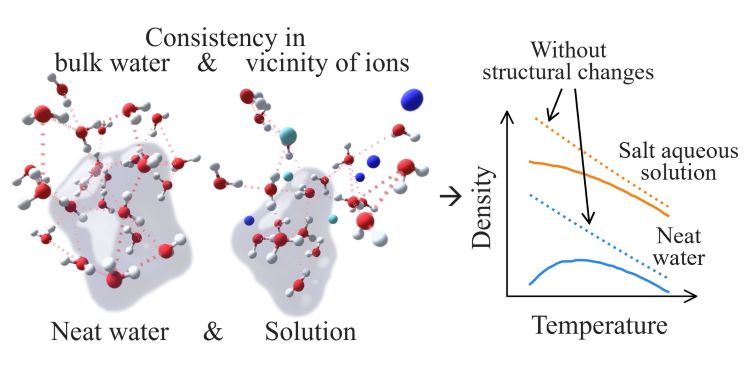
Structural indicators, also known as structural descriptors, including order parameters, have been proposed to quantify the structural properties of water to account for its anomalous behaviors. However, these indicators, mainly designed for bulk water, are not naturally transferrable to the vicinity of ions due to disruptions in the immediate neighboring space and a resulting loss of feature completeness. To address these non-bulk defects, we introduced a structural indicator that draws on the concept of clique number from graph theory and the criterion in agglomerative clustering, denoted as the average cluster number. This structural indicator aims to discern intrinsic structural characteristics within the water molecules regardless of the ions occupying the neighboring space, without requiring additional corrections. From molecular dynamics simulation results for neat water and salt aqueous solutions utilizing the TIP4P/2005 water model and the Madrid-2019 force field, we characterized the variations in densities with temperature using this network-based indicator, thereby demonstrating its practical utility. The findings suggest that at lower temperatures, the addition of ions disrupts the intrinsic structure of water molecules, with this effect diminishing as the temperature rises. Cations with larger charge density tend to induce stronger disruptions. This study highlights the importance of mitigating the impact of non-bulk defects before applying the indicators to analyze water’s intrinsic structural properties in solutions. By doing so, the relationship between changes in water structure and solution behaviors can be more accurately assessed.
简介 Brief introduction
结构特征量可以用于量化水的结构性,解释水的反常性质。然而,这些结构特征量主要针对体相水,并不一定能够直接迁移到离子附近的水分子,因为它们的最近邻空间和特征完整性受到影响。为了处理该边界效应,我们引入了一种名为“平均团簇数”的结构特征量。该结构特征量借鉴了图论中的团数(clique number)概念和层次聚类的准则,旨在揭示水分子的内在结构性,而不受离子占据邻近空间的影响,同时无需进行额外修正。
通过对使用了 TIP4P/2005 水分子模型和 Madird-2019 力场的纯水与溶液模拟结果进行分析,我们利用该结构特征量表征了溶液密度随温度的变化,从而说明了其实际应用价值。研究结果表明,在较低温度下,离子的加入将破坏水分子的内在结构性;随着温度升高,程度逐渐减弱。电荷密度更高的阳离子可能具有更强的结构破坏作用。该研究强调了在应用这些特征量分析溶液中水分子的内在结构性时缓解边界效应的重要性。而通过缓解边界效应,能够更准确地分析水的结构性和溶液性质的关联。
扫码关注立方体公众号,实时追踪课题组最新科研进展



