题目 Title
Drag Force on Submerged Flexible Vegetation in an Open-Channel Flow
期刊 Journal
Water Resources Research (IF=5.9)
作者 Author
Wang, J. Y.; He, G. J.; Huang, L.; Dey, S.; Fang, H. W.
摘要 Abstract
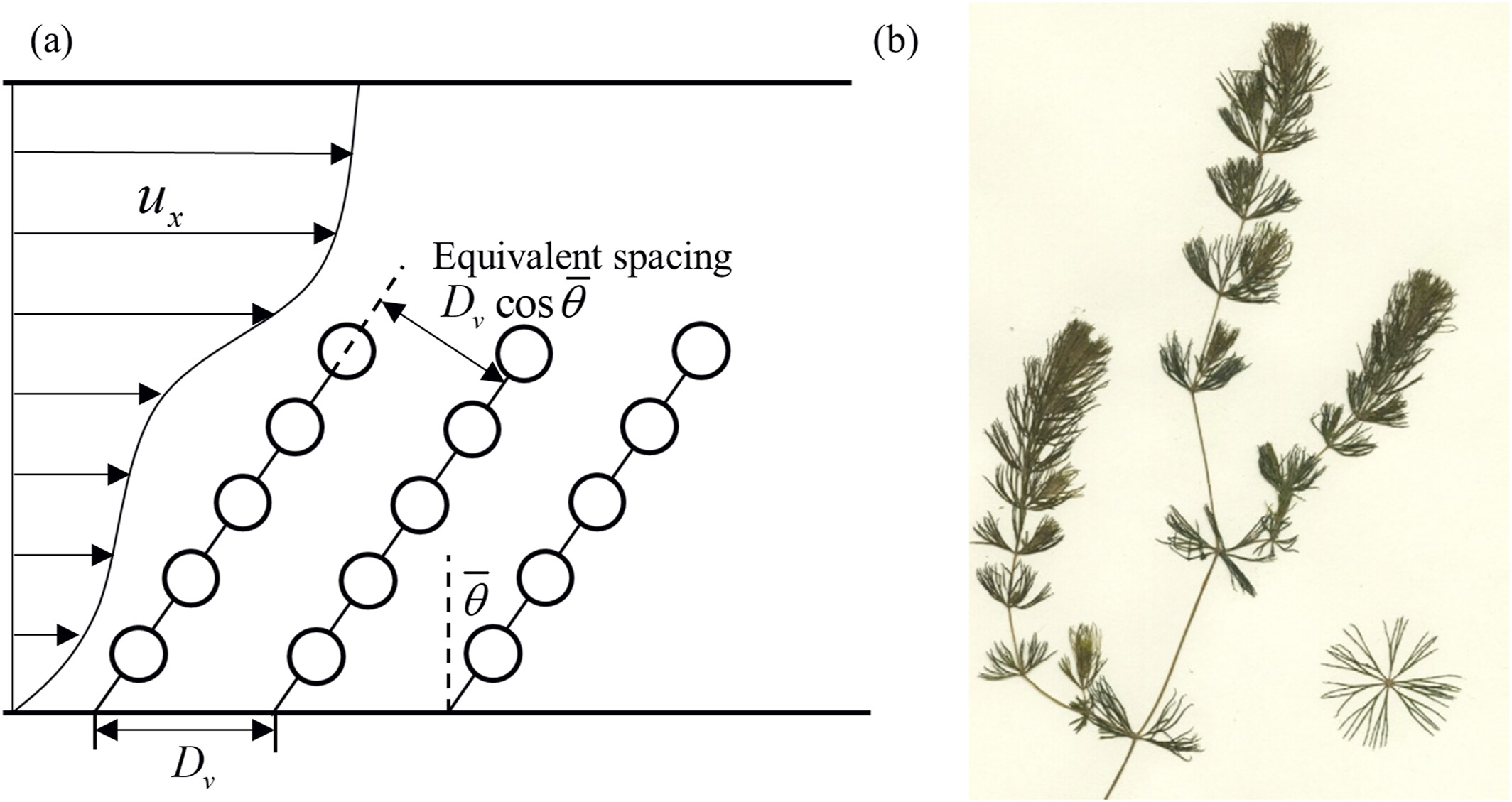
The movement of submerged flexible vegetation leads to an increase in resistance to the stream flow. In this study, a formula that can directly calculate the drag force on a highly flexible submerged vegetation, called Ceratophyllum, by using the vegetation swaying characteristics and the flow field information in a steady-uniform open-channel flow is derived. The drag force on submerged flexible vegetation is characterized by the time-averaged flow velocity, turbulence intensity, and the additional force arising from the vegetation swaying. Based on the results of the numerical models in the previous studies (Wang et al., 2022a, 2022b, , ), the drag coefficient is determined. It is revealed that the drag coefficient is influenced by a combination of factors, including the flow conditions, and the distribution and movement characteristics of vegetation. The drag coefficient decreases with an increase in velocity and is approximately linearly related to the cubic power of the bulk flow velocity. In the case of an inter-plant spacing of 0.5 times the initial plant height, the drag coefficient ranges from 10.72 to 2.11, as the Reynolds number varies from 20,000 to 50,000. Besides, the vegetation distribution density and the relative submergence influence the drag coefficient. In this context, the drag coefficient decreases linearly with an increase in the inter-plant spacing. For the Reynolds number equaling 50,000, the drag coefficient ranges from 2.11 to 2.02, when the inter-plant spacing varies from 0.5 to 2 times the plant height, and from 2.47 to 1.79, when the flow depth varies from 1.5 to 3 times the plant height.
简介 Brief introduction
沉水柔性植被的运动导致了水流阻力的增加。本研究推导了一个公式,可基于植物摆动特性和流场信息,直接计算一种高柔性沉水植物(金鱼藻)在均匀稳定明渠流中的拖曳力。沉水柔性植被的拖曳力由时均流速、湍流强度和植物摆动产生的附加力共同决定。基于先前研究(Wang et al., 2022)的数值模型结果,可确定拖曳系数。研究表明,拖曳系数受多种因素的影响,包括水动力学特征、植被空间分布和运动特性。拖曳系数随着流速的增加而减小,与流速的三次方近似成比例。当植株间距为初始植株高度的0.5倍时,雷诺数从20,000增加到50,000的情形下,拖曳系数从10.72减小到2.11。此外,植被分布密度和相对淹没深度也会影响拖曳系数。拖曳系数随着植株间距的增加线性减小。对于雷诺数为50,000的情形,当植株间距从植株高度的0.5倍增加到2倍时,拖曳系数从2.11减小到2.02;而当水深从植株高度的1.5倍增加到3倍时,拖曳系数从2.47减小到1.79。
扫码关注立方体公众号,实时追踪课题组最新科研进展



