题目 Title
Effects of Hydrogen Bond Networks on Viscosity in Aqueous Solutions
期刊 Journal
Journal of Physical Chemistry B (IF=2.8)
作者 Author
Gao, Y. T.; Wu, J.; Feng, Y. X.; Han, J. L.; Fang, H. W.
摘要 Abstract
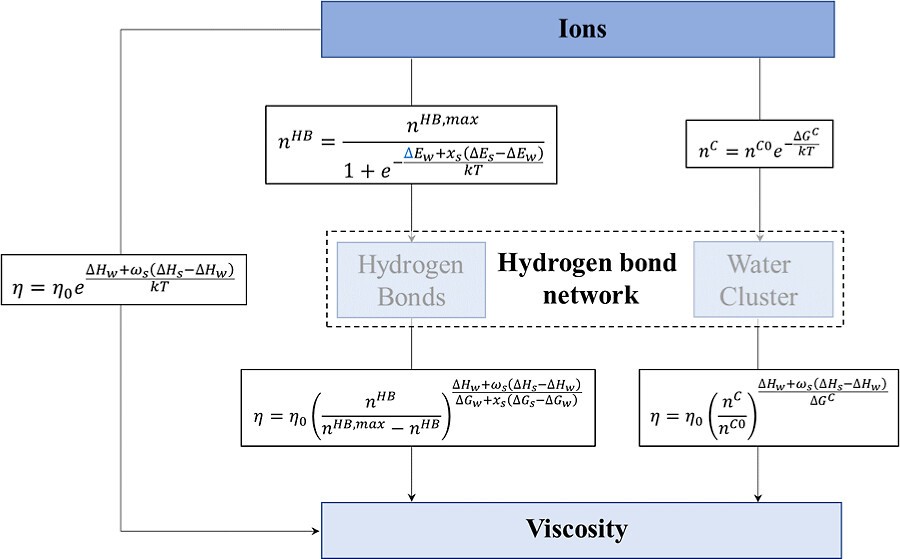
In aqueous solutions, the impact of ions on hydrogen bond networks plays a crucial role in transport properties. We used molecular dynamics simulations to explain how ions affect viscosity through structural changes. We developed a quantitative model to describe the effect of ions on viscosity. The model comprises two parts: the addition of ions alters hydrogen bond networks, and changes in hydrogen bond networks exponentially lead to changes in viscosity. The influence of ions on hydrogen bond networks involves the following mechanisms: first, ions can disrupt the tetrahedral structures within the first solvation shell into three-coordinated structures through substitution; second, structural changes within the first shells affect the global hydrogen bond network through electrostatic forces and the hindrance of ionic volumes. By analyzing the mechanisms of how hydrogen bond networks determine viscosity through the decomposition of viscosity, we found that the proportion of potential viscosity in aqueous solutions primarily increases due to the enhancement of non-hydrogen bonding interactions, and the proportion of hydrogen bonding viscosity decreases accordingly. Our results demonstrate that hydrogen bond networks are crucial for describing the changes in transport phenomena affected by external factors.
简介 Brief introduction
在水溶液中,离子对氢键网络的影响是决定溶液传输性质的关键因素。本研究使用分子动力学模拟揭示了离子如何通过改变结构影响粘性,并构建了一个定量描述模型。该模型包含两个核心部分:离子的加入改变了氢键网络,而氢键网络的变化引发了粘性指数级的改变。离子对氢键网络的影响主要通过以下两种机制实现:其一,离子通过取代作用破坏第一溶剂化壳层中的四面体结构,形成三配位结构;其二,第一溶剂化壳层中的结构变化通过静电相互作用和离子体积的阻碍作用进一步影响全局的氢键网络。通过对粘性进行分解分析探究氢键网络决定粘性的机制,我们发现,随着非氢键作用的增强,水溶液中势能粘性的占比逐渐增加,而氢键粘性的占比则相应减少。研究结果表明,氢键网络在描述传输性质受外部因素影响而改变的过程中起着重要作用。
扫码关注立方体公众号,实时追踪课题组最新科研进展



