题目 Title
Improved data assimilation for algal bloom dynamics simulation in the Three Gorges Reservoir using particle filter
期刊 Journal
Science of The Total Environment (IF= 8.6)
作者 Author
Huang, L.; Xu, X. Y.; Fang, H. W.; He, G. J.; Gao, Q. F.; Wang, K.; Gao, L.
摘要 Abstract
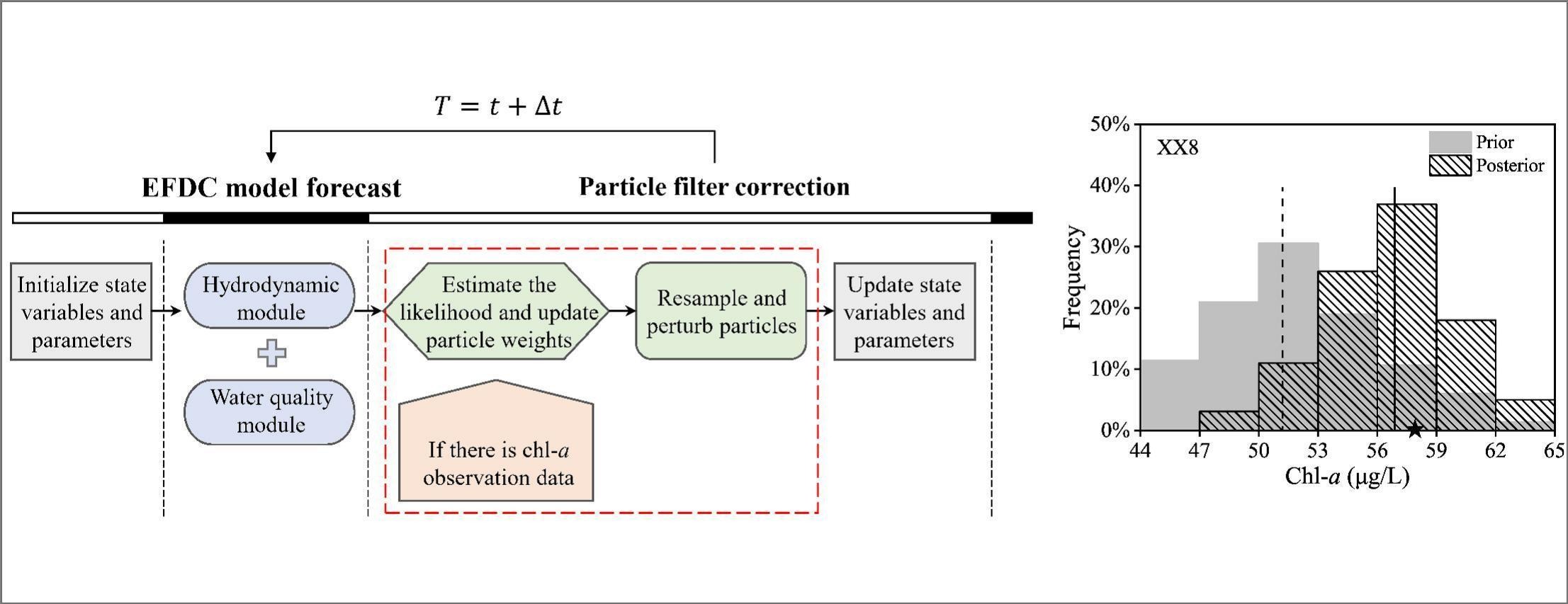
Algal blooms have been increasingly prevalent in recent years, especially in lakes and reservoirs; their accurate prediction is essential for preserving water quality. In this study, the observed chlorophyll a (chl-a) levels were assimilated into the Environmental Fluid Dynamics Code (EFDC) of algal bloom dynamics by using a particle filter (PF), and the state variables of water quality and model parameters were simultaneously updated to achieve enhanced algal bloom predictive performance. The developed data assimilation system for algal blooms was applied to Xiangxi Bay (XXB) in the Three Gorges Reservoir (TGR). The results show that the ensemble mean accuracy and reliability of the confidence intervals of the predicted state variables, including chl-a and indirectly updated phosphate (PO4), ammonium (NH4), and nitrate (NO3) levels, were considerably improved after PF assimilation. Thus, PF assimilation is an effective tool for the dynamic correction of parameters to represent their inherent variations. Increased assimilation frequency can effectively suppress the accumulation of model errors; therefore, the use of high-frequency water quality data for assimilation is recommended to ensure more accurate and reliable algal bloom prediction.
简介 Brief introduction
近年来,湖泊水库中水华暴发日益频繁,准确预测水华对于水质保护至关重要。本研究将观测到的叶绿素a浓度,通过粒子滤波方法同化到EFDC水华动力学模拟中,同时更新水质状态变量和模型参数,以提高水华预测能力。该水华数据同化系统被应用于三峡水库的香溪河库湾。结果表明,通过粒子滤波数据同化,叶绿素a浓度、磷酸盐、铵盐和硝酸盐等变量的平均预测精度、及其置信区间的可靠性,均得到显著提升。增加同化频率能够有效抑制模型误差的累积,故建议使用高频水质数据同化,以确保更为准确和可靠的水华预测。
扫码关注立方体公众号,实时追踪课题组最新科研进展



