题目 Title
Analytical model of contaminant advection, diffusion and degradation in capped sediments and sensitivity to flow and sediment properties
期刊 Journal
Journal of Hydrology (IF=6.4)
作者 Author
Chen, Z. L.; He, G. J.; Huang, L.; Shen, X. L.; Reible, D.; Fang, H. W.
摘要 Abstract
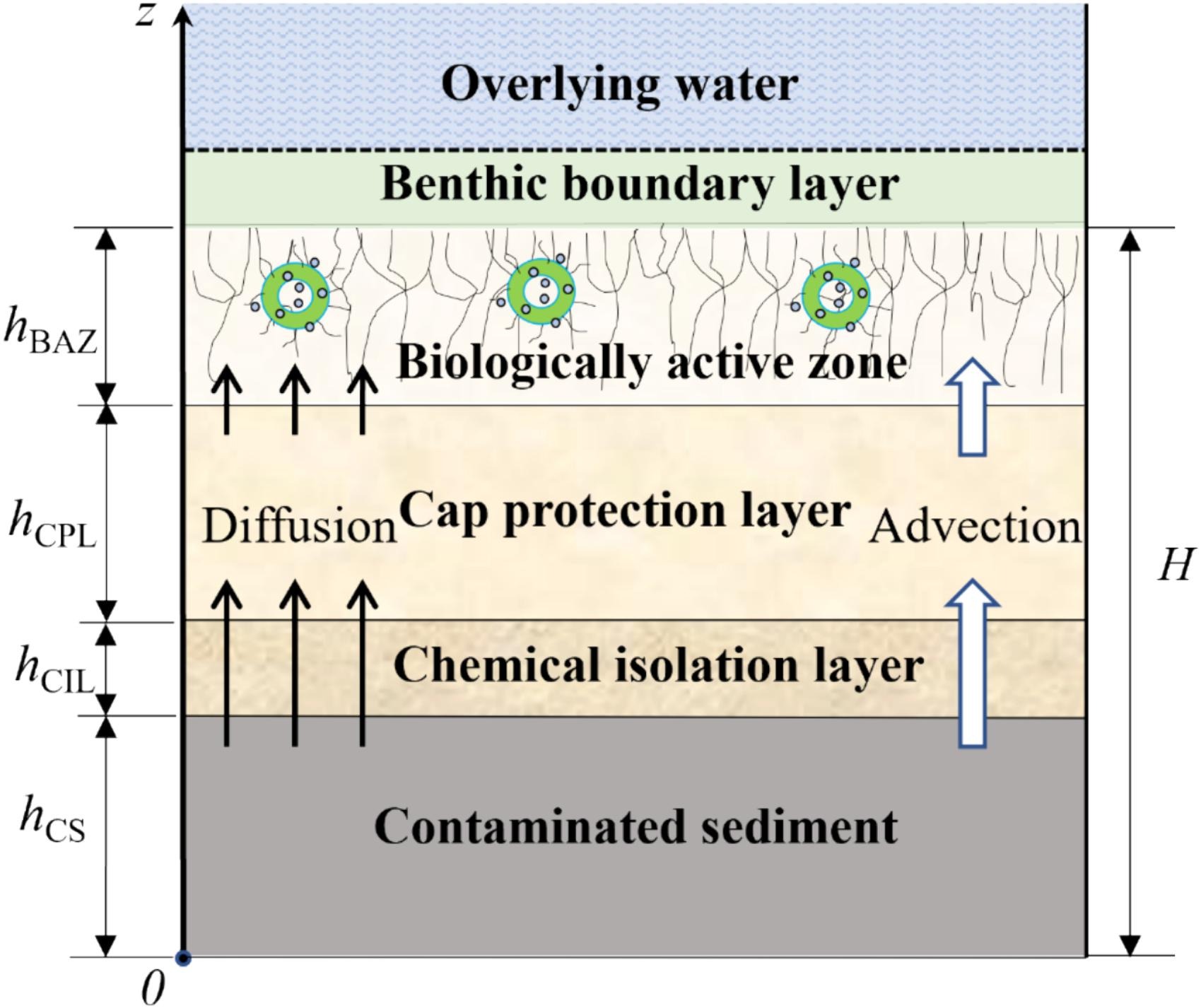
An analytical model is developed for contaminant advection-diffusion-degradation in a contaminant containment system of multiple layers of porous media such as a clean substrate or cap placed above contaminated sediment. Typically, sediment cap is modeled as a stratified system consisting of a biologically active zone (BAZ), cap protection layer (CPL), sorbent or chemical isolation layer (CIL), and contaminated sediment layer (CS). Diffusion, advection, linear equilibrium sorption, and first-order biodegradation processes are all included in this model. The proposed analytical solution is concise and easy to implement by introducing an innovative solution methodology combining the separation of variables and the transfer matrix method. The analytical solution is verified against existing analytical and numerical solutions. A comparative analysis of the two scenarios of treating the source as a constant concentration boundary and a finite initial concentration distribution is conducted. The solutions can be used for the design of a multi-layer containment system, verification of numerical models, and evaluation of experimental data. An analytical model can easily be used to understand the effects of key model parameters and the effects of the mass transfer coefficient at the benthic boundary layer, the biodegradation in BAZ, and the absorption capacity of CIL are investigated for diffusion-dominated and advection-diffusion scenarios. Results show that advection, adsorption and biodegradation significantly affect contaminant transport while mass transfer in the benthic boundary layer is important only under some circumstances.
简介 Brief introduction
本文针对层状多孔介质污染物阻隔系统(例如:污染底泥上覆洁净基底或覆盖层)中的污染物对流-扩散-降解过程,开发了一种解析模型。通常情况下,沉积物覆盖层会被模拟为一个分层系统,包括生物活性区(BAZ)、覆盖保护层(CPL)、吸附或化学隔离层(CIL)、以及污染沉积物层(CS)。该模型包含了扩散、对流、线性平衡吸附和一阶生物降解过程。通过引入一个结合变量分离法和传递矩阵法的创新性求解方法,提出了一个极其简洁且易于实现的解析解。该解析解的正确性通过与现有的解析解和数值解对比得到验证。文中针对两种情形(将污染源分别视为恒定浓度边界和有限初始浓度分布)进行了全面对比分析。该解析解可用于多层污染物阻隔屏障系统的设计、数值模型的验证以及实验数据的评估。该解析模型可以便捷地用于理解关键模型参数的影响,在扩散主导和对流-扩散情形下,底栖边界层的质量传递系数、BAZ中的生物降解、以及CIL的吸附能力的影响都得到探究。结果表明,对流、吸附和生物降解对污染物的运移有显著影响,而底栖边界层的质量传递仅在某些情况下具有重要作用。
扫码关注立方体公众号,实时追踪课题组最新科研进展



