题目 Title
Influence of Bioroughness Density on Turbulence Characteristics in Open-Channel Flows
期刊 Journal
Journal of Hydraulic Engineering (IF=2.3)
作者 Author
Chen, Z. H.; He, G. J.; Fang, H. W.; Liu, Y.; Dey, S.
摘要 Abstract
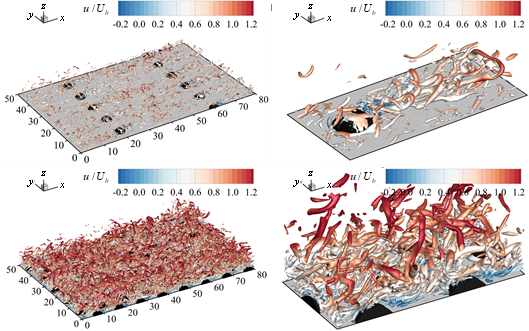
Bioroughness plays an important role in modifying the velocity and sediment flux near the riverbed. It is therefore pertinent to study the influence of benthic fauna on the bed forms. To this end, large-eddy simulations are performed to investigate the influence of the arrays of mounds and their density on the turbulence characteristics in an open-channel flow. The simulated distributions of the time-averaged streamwise velocity and the turbulence intensity are in good agreement with the experimental data. Four numerical simulations are performed with varying streamwise spacings of mounds. Details of the time-averaged and instantaneous flow velocities are analyzed by multiple visualization methods, and the effects of the bioroughness density on the equivalent roughness height and the Darcy–Weisbach friction factor are quantified. The time-averaged flow in the wake of the mounds is characterized by a symmetric pair of vortices. The mounds behave like bluff bodies, increasing the riverbed roughness and heterogeneity in the flow environment. An increase in mound density is to promote the development of secondary currents and to increase the dispersive stress near the bed. The peaks of the Reynolds shear stress distributions decrease in both the streamwise and vertical directions for the high-density case due to a blockage effect. The instantaneous flow features, in the form of various turbulence structures, are generated near the top edge and the wake zone of mounds. The spacing between low-speed streaks decreases with an increase in equivalent roughness height. Multifrequency behavior that is observed is a result of shear layer roll-up from the edges of mounds and the flapping of wake. Finally, two formulas for equivalent roughness height and Darcy–Weisbach friction factor are proposed involving the bioroughness density and height. The findings demonstrate the effects of the bioroughness on the near-bed turbulence characteristics and sediment stability.
简介 Brief introduction
底栖生物粗糙元在改变河床附近的流速和泥沙输运方面起着重要作用。因此,研究底栖动物对床面形态的影响具有重要意义。为此,本文采用大涡模拟(LES)方法,研究了生物粗糙元排列与密度对明渠流动湍流特性的影响。模拟的时均流向速度和湍流强度的分布与实验数据吻合良好。通过改变生物粗糙元的流向间距共进行了四组数值模拟,并采用多种可视化方法分析了时均与瞬时流速的细节,同时量化了生物粗糙元密度对等效粗糙高度和Darcy-Weisbach摩擦因子的影响。
粗糙元尾流中的时均流动特征表现为对称的涡旋,其类似钝形物体,增加了河床粗糙度和流动环境的异质性。生物粗糙元密度的增加将促进二次流的发展,提高床面附近的分散应力。在高密度情况下,由于阻塞效应,雷诺切应力分布的峰值在流向和垂向上均有所降低。瞬时流动特征表现为在粗糙元顶部边缘区域和尾流区域生成的多种湍流结构。随着等效粗糙高度的增加,低速带之间的间距减小。观察到的多频率行为来源于粗糙元边缘区域剪切层的卷起及尾流摆动。最后,提出了两条包含生物粗糙元的密度和高度的等效粗糙高度和Darcy-Weisbach摩擦因子的公式。研究结果揭示了生物粗糙元对近床面湍流特性和泥沙稳定性的影响。
扫码关注立方体公众号,实时追踪课题组最新科研进展



