题目 Title
Structural Effects of Water Clusters on Viscosity at High Shear Rates
期刊 Journal
The Journal of Chemical Physics (IF=4.4)
作者 Author
Gao, Yitian; Wu, Jian; Feng, Yixuan; Han, Jiale; Fang, Hongwei
摘要 Abstract
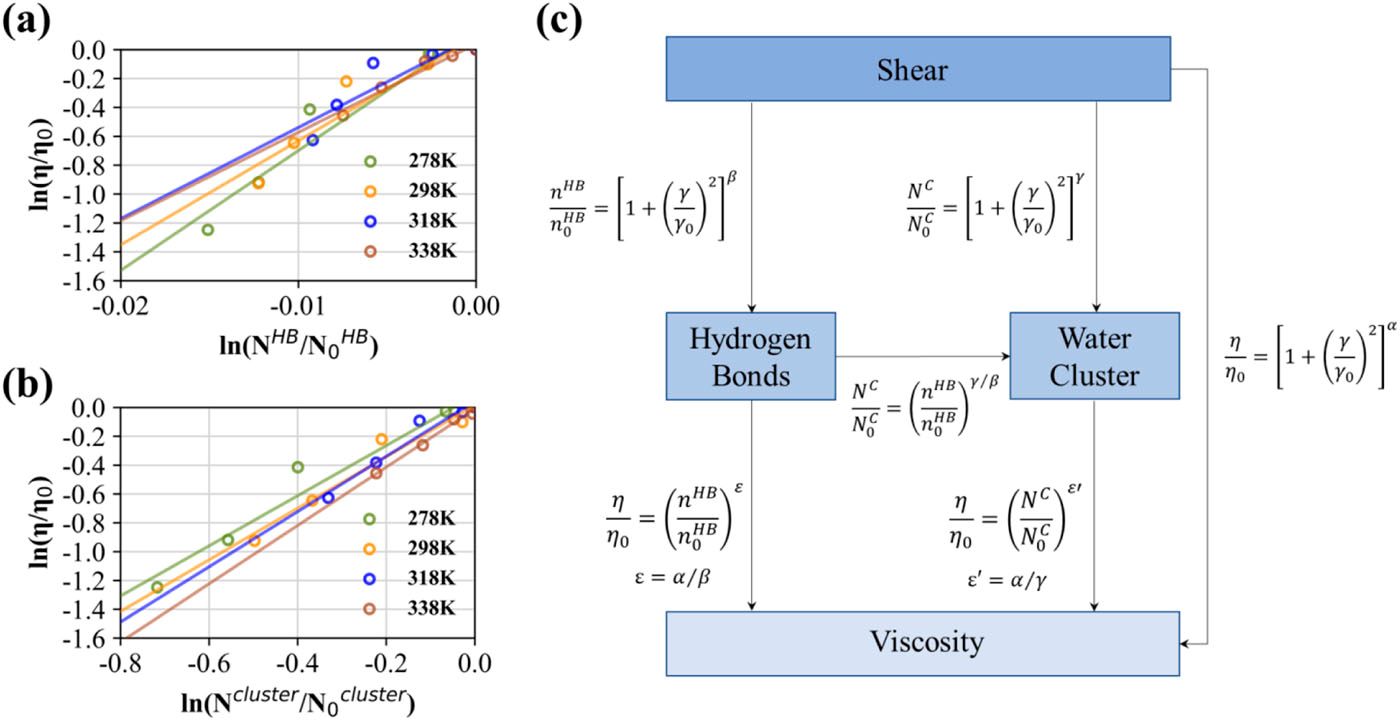
In this study, we use molecular dynamics simulations of liquid water to investigate how shear thinning affects the viscosity of liquid water by structural changes of the hydrogen bond network. The effect of shear on viscosity can be divided into two parts: shear-induced destruction of the hydrogen bond network and the influence of the water structure on shear viscosity. First, strong shear destroys tetrahedral structures and thus reduces the connectivity of the hydrogen bond network. It is mainly because shear deformation, characterized by compression and expansion axes, respectively, triggers the destruction and formation of hydrogen bonds, resulting in anisotropic effects on water structures. At the same time, shear destroys large clusters and enhances the formation of small ones, resulting in a decrease in average cluster sizes. Second, the change of viscosity obeys a power law relationship with the change of hydrogen bond structures, highlighting a one-to-one correspondence between structure and property. Meanwhile, in order to explain why the structure affects viscosity, we define hydrogen-bond viscosity and find that the cooperative motion of the water structures can promote momentum transfer in the form of aggregations. Hydrogen-bond viscosity accounts for 5%-50% of the total viscosity. Our results elucidate that water structures are the important structural units to explain the change of water properties.
简介 Brief introduction
在本研究中,我们利用液态水的分子动力学模拟,研究剪切稀释如何通过改变氢键网络结构影响液态水的粘性。剪切对粘性的影响可以分为两个部分:剪切引起的氢键网络破坏和水结构对剪切粘性的影响。第一,强剪切破坏了四面体结构,从而降低了氢键网络的连通性。这主要是因为剪切变形引起了氢键的破坏和形成(分别通过压缩轴和膨胀轴表征),对水结构产生了各向异性的影响。同时,剪切破坏了大型团簇,促进了小型团簇的形成,导致平均团簇尺寸减小。第二,粘性的变化与氢键结构的变化之间遵循幂律关系,凸显了结构与性质之间的一一对应关系。为了解释结构影响粘性的原因,我们定义了氢键粘性,并发现水结构的协同运动能够以聚集的方式促进动量传递。氢键粘性占总粘性的5%-50%。结果表明,水结构是解释水性质变化的重要结构性单元。
扫码关注立方体公众号,实时追踪课题组最新科研进展



