题目 Title
Fluid structure interaction in a flexible vegetation canopy in an open channel.
期刊 Journal
Journal of Fluid Mechanics (IF=4.245)
作者 Author
Wang JY; He GJ; Dey S; Fang HW
摘要 Abstract
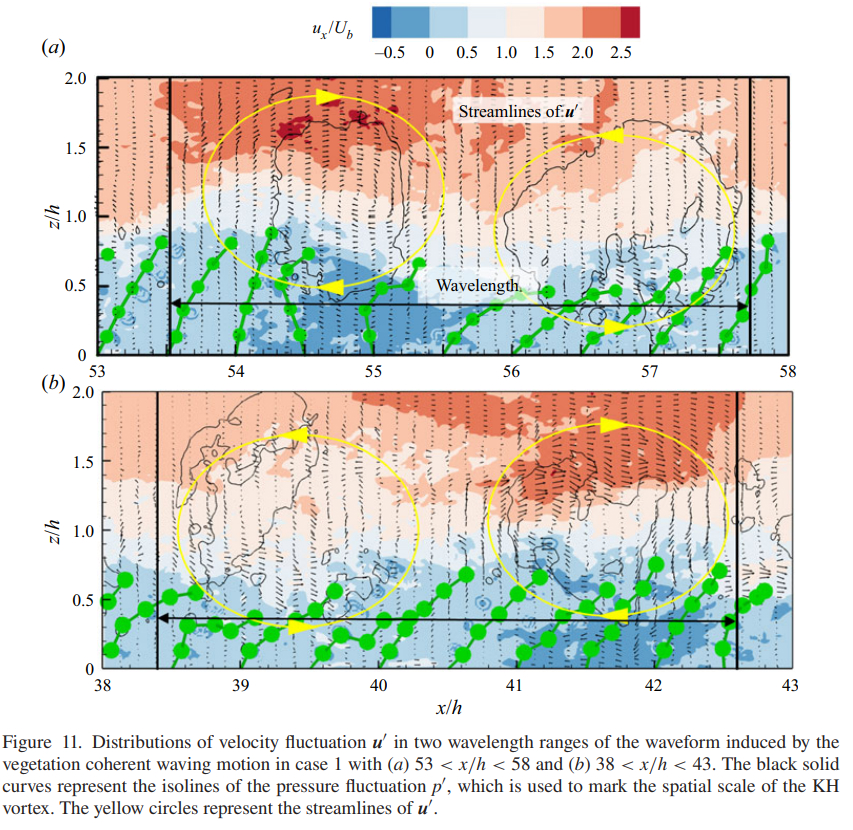
Submerged flexible vegetation occupies the core of aquatic ecosystem research. Hydrodynamics of submerged flexible vegetation and its interaction with the flow in an open channel are of great significance in studying the mass and momentum transports in the flow. In this study, a numerical model for highly flexible vegetation based on large eddy simulation and the immersed boundary method was used to simulate the flow-vegetation interaction. It is recognised that alternate vortices with opposite sense rotations appear at the flow-vegetation interface. These vortices prompt the vegetation canopy to have wave-like coherent waving motion, commonly called the monami phenomena. The spatial scale and the spreading velocity in the streamwise direction of these vortices determine the wavelength, frequency and amplitude of the vegetation coherent waving motion. In this study, the fast Fourier transform method was applied to analyse the factors affecting the characteristics of the vegetation coherent waving motion. It is revealed that, as the flow velocity increases, the wavelength of the coherent waving motion decreases, while the frequency and amplitude increase. Besides, as the vegetation spacing increases, the wavelength and amplitude of the coherent waving motion increase, but the frequency decreases. Furthermore, an increase in the relative density of vegetation magnifies the amplitude of coherent waving motion without affecting the wavelength and frequency.
简介 Brief introduction
沉水柔性植被的水动力学及其与明渠水流的相互作用对于研究水流中的物质和动量的传输具有重要意义。本研究基于大涡模拟(LES)和浸没边界法(IBM)建立了高柔性植被数值模型,模拟了水流-沉水柔性植被的相互作用。研究发现,在水流-植被界面处形成了交替分布的旋转方向相反的涡旋。这些涡旋使植被冠层出现周期性相干波动,这通常被称为“monami”现象。涡旋的空间尺度和沿顺流向的传播速度决定了植被相干波动的波长、频率和振幅。利用快速傅里叶变换(FFT)分析影响植被相干波动运动特征的因素,结果表明:随着流速的增加,相干波动的波长减小,而频率和振幅增加;随着植被间距的增加,相干波动的波长和振幅增加,而频率降低;随着植被相对密度的增加,振幅增加,而波长和频率不受影响。
扫码关注立方体公众号,实时追踪课题组最新科研进展



