题目 Title
Multidimensional ecosystem assessment of Poyang Lake under anthropogenic influences.
期刊 Journal
Ecological Modelling (IF=3.512)
作者 Author
Meng JN; Fang HW; Huang L; He GJ; Liu XB; Xu CY; Wu XH; Scavia D
摘要 Abstract
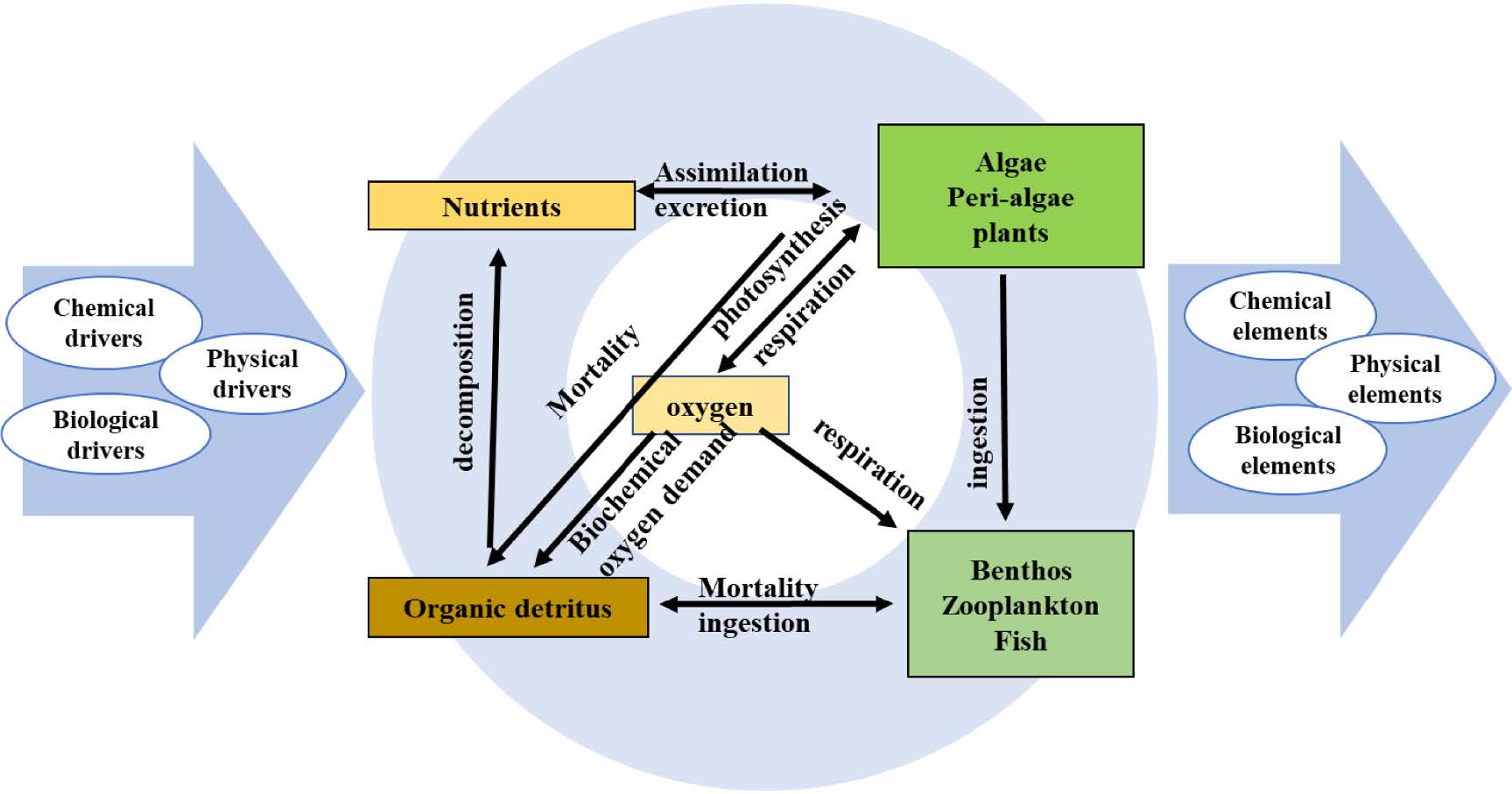
Watershed anthropogenic activities, including pollutant discharge, sand mining, and upstream reservoir operation, have increased nutrient loads and decreased water levels and sediment concentrations in Poyang Lake, and thus affected the aqueous ecosystem. In this study, we developed an ecological model from the framework of AQUATOX to simulate the physical, chemical, and biological evolution of Poyang Lake under watershed anthropogenic influences, and used model output for a multidimensional ecosystem assessment of ecosystem structure, function, service, material flow, temporal dynamics, and collapse probability. The potential impacts of a proposed Poyang Lake water conservancy project (PYWCP) to build a sluice near the outlet of Poyang Lake to regulate lake level were explored. Results show that the watershed anthropogenic activities have worsened the Poyang Lake ecosystem. Specifically, the phytoplankton biomass increased, while benthos and fish decreased; the exergy, capacity of nutrient change, and the total biomass-gross primary production ratio decreased; as the lake’s volume decreased, fishes’ trophic levels and food web robustness decreased, the food web shrank, single species dependence increased, and ecosystem stability decreased. The PYWCP could mitigate most of these effects, however, it would not recover Poyang Lake to historical conditions, and close monitoring with attention to sluice operational scheduling are required.
简介 Brief introduction
构建了鄱阳湖水体的地球物理化学生物模型,对鄱阳湖历史、现状和未来(建闸)情况进行模拟,并通过多维度生态系统分析,分析了鄱阳湖在流域人类活动影响下的现有生态系统变化,以及建闸会带来的可能影响。结果表明,流域人类活动加剧了鄱阳湖生态系统的恶化,主要表现在浮游植物生物量增加,底栖生物和鱼类生物量减少;生态系统的能值、环境容量和单位生产力支撑的生物量降低;鱼类的营养水平和食物网的鲁棒性降低,食物网缩小,物种依赖不均匀程度增加,生态系统稳定性下降。鄱阳湖水利枢纽工程虽能缓解上述大部分影响,但不能使鄱阳湖恢复到历史水平,且需密切监测并注意水闸运行调度。
扫码关注立方体公众号,实时追踪课题组最新科研进展



