题目 Title
Parameter uncertainty and sensitivity analysis of the three Gorges Reservoir and Xiangxi River EFDC model.
期刊 Journal
Journal of Hydrology (IF=5.722)
作者 Author
Xu S; He GJ; Fang HW; Bai S; Wu XH
摘要 Abstract
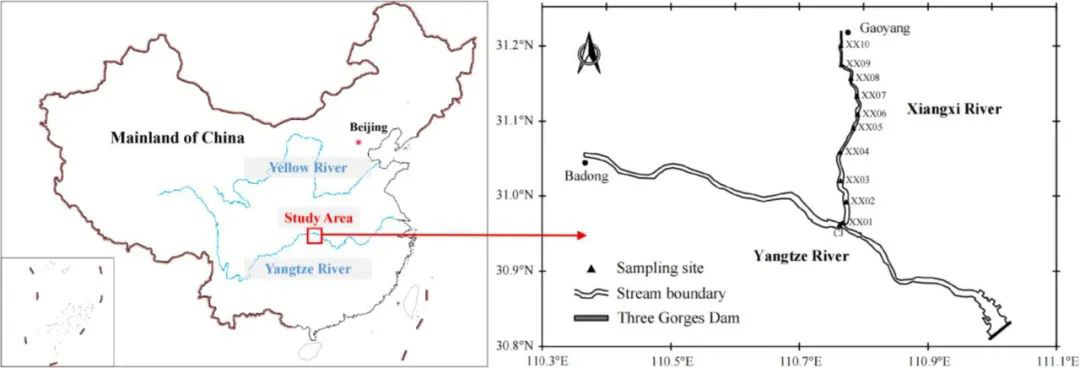
Water quality models are decision support tools for the planning and management of the aquatic environment. However, the application of the model needs an intricate calibration process due to the various ranges of numerous parameters. To help improve the accuracy of model simulation, and reduce the workload of parameter adjustment to similar surface waters, parameter uncertainty and sensitivity analyses of the Environmental Fluid Dynamics Code (EFDC) model were carried out in this study. The EFDC model was first calibrated and simulation results agree well with the measured data. The Generalised Likelihood Uncertainty Estimation (GLUE) and Regional Sensitivity Analysis (RSA) methods are then applied to analyze the uncertainty and sensitivity of the model. Eighteen kinetic parameters related to algae and organic matter are filtered and analyzed. The results show that the sensitivities of the model to eighteen input parameters are significantly different. The modeled algae levels measured as chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) are highly sensitive to the optimal growth rate and the maximum basal metabolism rate of cyanobacteria (BMRc and PMc), with the Sensitivity Indices (SI) at 0.66 and 0.78, respectively. The inorganic nutrient levels (phosphorus, nitrate nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen) are highly sensitive to minimum respiration rates of corresponding dissolved organic matter (KDP and KDN) with SIs at 0.78, 0.56 and 0.88. Dissolved oxygen (DO) is highly sensitive to PMc and KDC, with their SIs at 0.66 and 0.85, respectively. The uncertainty interval is focused on the periods of high algae concentration. The simulated uncertainty in the surface water is higher than that in middle-layer water, and might be related to algal transport processes like settlement and horizontal transport. The results of the uncertainty and sensitivity analyses in this study support a better understand of the modeling mechanisms and provide scientific guidance for calibration in similar waterbodies.
简介 Brief introduction
水质模型是规划和管理水生环境的决策支持工具。然而,由于众多参数的范围不同,模型应用需要一个复杂的校准过程。为提高模型仿真的准确性,减少对类似地表水进行参数调整的工作量,对环境流体动力学代码(EFDC)模型进行了参数不确定性和灵敏度分析。我们对EFDC模型进行了校准,使模拟结果与测量数据吻合,然后应用广义似然不确定性估计(GLUE)和区域敏感性分析(RSA)方法来分析模型的不确定性和参数灵敏度。一共筛选并分析了与藻类和有机物相关的18个动力学参数。结果表明,模型对18个输入参数的敏感度存在显著差异。用叶绿素a(Chl-a)表示的藻类模拟结果对蓝藻的最佳生长速率和最大基础代谢速率(BMRc和PMc)高度敏感,敏感性指数(SI)分别为0.66和0.78。无机营养盐(磷、硝态氮和氨氮)对相应元素的溶解有机物的最小呼吸速率高度敏感(KDP和KDN),敏感性指数分别为0.78、0.56和0.88。溶解氧(DO)对PMc和KDC高度敏感,其敏感性指数分别为0.66和0.85。模拟结果的不确定区间集中在藻类高浓度时期。表水中模拟的不确定性高于中层水的不确定性,这可能与藻类的迁移过程(沉降和水平输移)有关。本研究中的不确定性和敏感性分析结果有助于更好地理解建模机制,并为类似水体的校准提供科学指导。
扫码关注立方体公众号,实时追踪课题组最新科研进展



