题目 Title
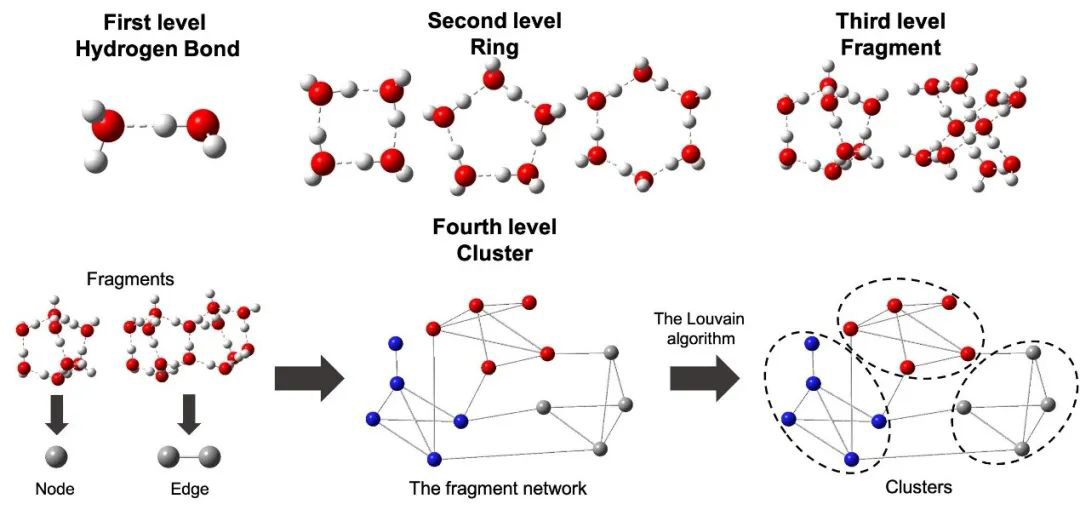
Hierarchical clustering analysis of hydrogen bond networks in aqueous solutions.
期刊 Journal
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics (IF=3.676)
作者 Author
Feng, YX; Fang, HW; Gao, YT; Ni, K
摘要 Abstract
To understand the relation between the macroscopic properties and microscopic structure of hydrogen bond networks in solutions, we introduced a hierarchical clustering method to analyze the typical configurations of water clusters in this type of network. Regarding hydrogen bonds as frames, the rings, fragments and clusters are defined and analyzed to provide a comprehensive perspective for the distributional and dynamic characteristics of the hydrogen-bonding network in NaCl solution at different concentrations. The properties of the radial distribution function and hydrogen bonds are first analyzed. Destruction and shorter lifetimes of hydrogen bonds are observed in solutions. In further analysis of the two-dimensional configuration, i.e., ring, and three-dimensional configuration, i.e., fragment, the average number, size and lifetime of these structures consistently decrease as the concentration increases. Ionic effects on disrupting rings and fragments are significant in the first hydration shell, especially with sodium cations, and these effects weaken beyond the first hydration shell. Regarding the clusters obtained using the Louvain algorithm, our results indicate that clusters break and become smaller as the NaCl concentration increases. The presence of ions also leads to the isolation of clusters and therefore the inhibition of changes. The lifetime of clusters increases with NaCl concentration, indicating the slowed breakage and reformation of clusters in NaCl solutions. This method can be further applied to quantitatively characterize hydrogen bond networks to elucidate more properties of aqueous solutions.
简介 Brief introduction
为了探索溶液中氢键网络微观结构和宏观性质之间的关系,本文引入了分层聚类方法来分析氢键网络中水分子团簇的典型结构。以氢键为骨架,对环结构、片元结构和团簇结构进行定义和分析,从一个更全面的角度分析不同浓度NaCl溶液中氢键网络的结构分布和动态特征。首先分析径向分布函数和氢键分布性质,发现相对于纯水,NaCl溶液中氢键网络结构受到破坏,呈现出更短的寿命。在对二维结构(即环)和三维结构(即片元)的进一步分析中,发现这些结构的平均数量、尺寸和寿命随着溶液浓度的增加而不断降低。离子对结构的破坏作用在第一个水合壳层中尤为明显,特别是钠离子,这种破坏作用在第一个水合壳层之外有所减弱。基于Louvain算法获得的团簇结构表明,随着NaCl浓度的增加,团簇结构会破裂,尺寸减小。同时,离子的存在会导致团簇之间分隔,从而抑制团簇之间的交换变化。团簇的寿命随着NaCl浓度的增加而增加,表明在NaCl溶液中团簇的破坏和重新形成过程减缓。该方法可进一步应用于定量表征氢键网络结构,以阐明水溶液的更多性质。
扫码关注立方体公众号,实时追踪课题组最新科研进展



