题目 Title
Effect of secondary currents on the flow and turbulence in partially filled pipes.
期刊 Journal
Journal of Fluid Mechanics (IF=3.627)
作者 Author
Liu Y; Stoesser T; Fang HW
摘要 Abstract
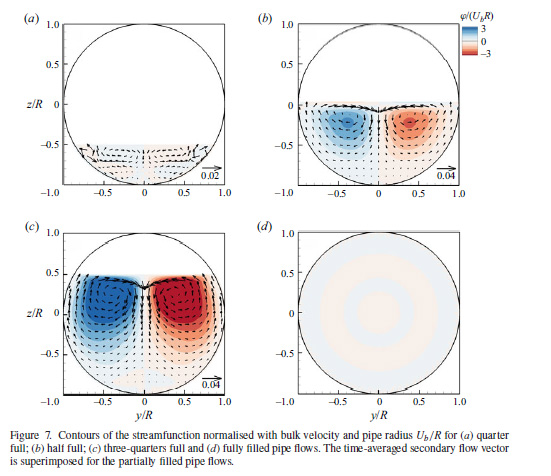
Large-eddy simulations of turbulent flow in partially filled pipes are conducted to investigate the effect of secondary currents on the friction factor, first- and second-order statistics and large-scale turbulent motion. The method is validated first and simulated profiles of the mean streamwise velocity, normal stresses and turbulent kinetic energy (TKE) are shown to be in good agreement with experimental data. The secondary flow is stronger in half- and three-quarters full pipes compared with quarter full or fully filled pipe flows, respectively. The origin of the secondary flow is examined by both the TKE budget and the steamwise vorticity equation, providing evidence that secondary currents originate from the corner between the free surface and the pipe walls, which is where turbulence production is larger than the sum of the remaining terms of the TKE budget. An extra source of streamwise vorticity production is found at the free surface near the centreline bisector, due to the two-component asymmetric turbulence there. The occurrence of dispersive stresses (due to secondary currents) reduces the contribution of the turbulent shear stress to the friction factor, which results in a reduction of the total friction factor of flows in half and three-quarters full pipes in comparison to a fully filled pipe flow. Furthermore, the presence of significant secondary currents inhibits very-large-scale motion (VLSM), which in turn reduces the strength and scales of near-wall streaks. Subsequently, near-wall coherent structures generated by streak instability and transient growth are significantly suppressed. The absence of VLSM and less coherent near-wall turbulence structures is supposedly responsible for the drag reduction in partially filled pipe flows relative to a fully filled pipe flow at an equivalent Reynolds number.
简介 Brief introduction
本文采用大涡模拟计算方法研究了水深对圆形断面明渠紊流结构的影响。基于湍动能平衡方程,揭示了断面二次流的产生机理:壁面-水面交界处的应力不均匀性;采用二维阻力系数分解方法,发现了二次流的减阻效应;采用能谱分析、相关性分析等方法详细阐释了二次流对超大规模水流运动和近壁面相干结构的抑制作用,进而解释了该减阻效应。研究结果完善了明渠二次流的相关理论,有助于开发低能耗的圆管输送新技术。
扫码关注立方体公众号,实时追踪课题组最新科研进展



