题目 Title
Impact of turbulence and secondary flow on the water surface in partially filled pipes.
期刊 Journal
Physical of Fluids (IF=3.521)
作者 Author
Liu Y; Stoesser T; Fang HW
摘要 Abstract
With the goal to explore the effects of natural bed roughness on bedload transport, numerical simulations of flow and particle saltation are carried out with varying bed roughness and particle spatial density. A combination of Eulerian and Lagrangian point-particle methods is applied to solve the equations of motion of the fluid and the particles within the large-eddy simulation framework. Flows over smooth and rough beds with four particle densities are considered. As the bed roughness increases, there is a leftward shift of the double-averaged streamwise velocity profiles against dimensionless vertical distance, which is scaled with the bed roughness height, an upward shift of the peak values of double-averaged Reynolds stresses, and a fragmentation and disappearance of coherent structures in the form of high-speed and low-speed near-bed streaks. These observations are consistent with those of previous studies. As the bed roughness increases, the mean resting time of saltating particles increases, however the particles' saltation length, velocity, and angular velocity decrease, while their saltation height remains almost unchanged. Saltation height, saltation length, particle angular velocity, and resting time exhibit linear, gamma, normal, and exponential distributions, respectively. Further, as the bed roughness increases, the kurtosis and skewness of some particle parameters vary, and the particle velocity shifts from a symmetrical normal to an asymmetrical gamma distribution.
简介 Brief introduction
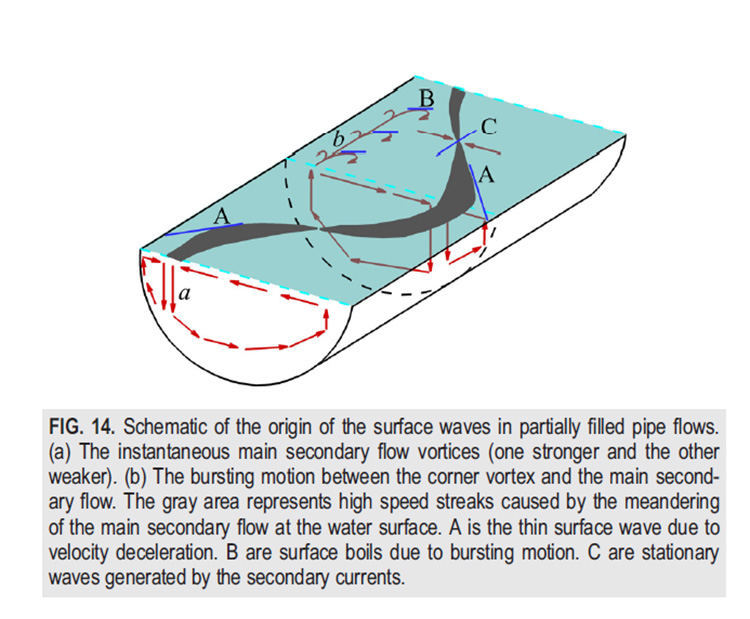
本文采用大涡模拟计算方法研究了不同水深情况下,圆形断面二次流对自由水面波纹结构的影响。通过本征正交分解、能谱分析和波数频谱分析等方法,分析了水面波纹和紊流流场的相互作用,发现了两种新的、与二次流流动相关的水面波纹结构,并依据其产生和传播机制将水面波纹划分为三种类型:(1)水沸波,(2)二次流横向摆动波,(3)二次流交汇波。其中二次流横向摆动波和二次流交汇波的波长明显大于水沸波。而随着水深的增加,二次流横向摆动波的强度逐渐降低,水沸波和二次流交汇波的强度逐渐增强。
扫码关注立方体公众号,实时追踪课题组最新科研进展



