题目 Title
Phosphorus transport in the Three Gorges Reservoir over the past two decades.
期刊 Journal
Journal of Hydrology (IF=5.722)
作者 Author
Zeng, X; Huang, L; He, GJ; Wang, DC; Wu, XH; Fang, HW
摘要 Abstract
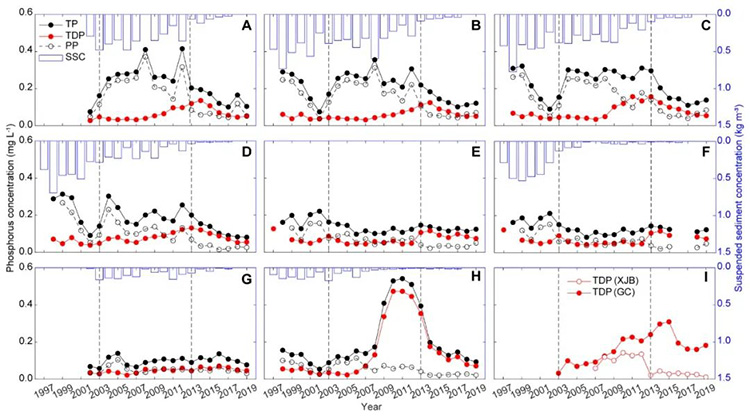
Phosphorus (P) is an essential nutrient in aquatic ecosystems and its dynamics in river systems are greatly affected by human activities. Using in situ measurements of water discharge (Q), suspended sediment concentrations (SSC), and concentrations (C) of total P (TP), particulate P (PP), and total dissolved P (TDP) from 1997 to 2017, the combined effects of cascade reservoirs operation and anthropogenic emissions on P transport in the Three Gorges Reservoir (TGR) has been discussed. The whole period was divided into three sequent periods of January 1997 to May 2003 (period 1), June 2003 to September 2012 (period 2), and October 2012 to December 2017 (period 3), corresponding to the period prior to impoundment of the TGR, during filling of the TGR and prior to the closure of the upstream dams, and after the impoundment of the upstream reservoirs, respectively. Results showed that the P concentrations were positively skewed and generally followed the three-parameter gamma distribution or three-parameter lognormal distribution, although the latter performs slightly better than the former. There was significant difference for SSC, TP, PP, and TDP between adjacent periods but not for Q. The SSC, TP, and PP presented downward trends during the periods affected by cascade reservoirs impoundment, while the TDP increased in period 2 especially after 2007 and decreased in period 3 as a combined result of the upstream reservoirs regulation and the pollution management in the tributaries. For the monthly variation, the SSC, TP, and PP became more evenly distributed throughout the year after the impoundment of cascade reservoirs, while the TDP tended to show a pattern of “higher in dry season and lower in flood season”. The C-Q relationships indicate that the TP in the TGR was positively correlated with Q (transport limited), while negatively with Q for TDP (source limited). Generally, the TP, PP, and TDP were positively correlated with both SSC and anthropogenic P emissions, thus, the P concentrations declined with sediment retention in the reservoir but increased with time due to the increasing pollutant emissions. The P dynamics were better depicted after considering the effects of sediment and pollutant emissions than using a simple C-Q relationship.
简介 Brief introduction
本文基于三峡库区近二十年的流量、含沙量、总磷和溶解磷浓度实测资料,利用方差分析、趋势检验和线性回归等方法,分析了库区磷浓度的时空分布特征,揭示了磷浓度与流量、含沙量等变量之间的关系,探讨了污染物排放(如上游支流磷矿污染)和梯级水库建设这两大人类活动因素对库区磷输移的综合影响。本文的研究结果对于理解人类干扰下大江大河的磷素动态和水生态环境治理具有一定的参考价值。
扫码关注立方体公众号,实时追踪课题组最新科研进展



