题目 Title
Effects of bedform migration on nutrient fluxes at the sediment-water interface: a theoretical analysis.
期刊 Journal
Environmental Fluid Mechanics (IF=2.551)
作者 Author
Huang, L; Gao, QF; Fang, HW; He, GJ; Reible, D; Wang, DC; Wu, XH
摘要 Abstract
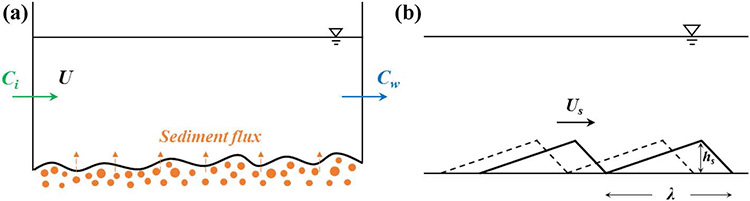
Nutrient fluxes at the sediment water interface are essential for water quality and aquatic ecosystems. In this study, a unified expression for the sediment nutrient flux under different controlling modes is proposed by analytically solving the first-order linear partial differential equations describing nutrient transport in the sediment layer and overlying water. In particular, the analytical expression for the sediment nutrient flux due to bedform migration is derived, and the effects of bedform parameters, water depth, and sediment size are explored. With increasing flow velocity, the controlling mode of the sediment nutrient flux changes from diffusion to sand wave motion and then bed erosion, resulting in a significant increase in the flux. The water depth and sediment size indirectly affect the sediment nutrient flux by changing the critical velocity and the dimension and migration velocity of the sand waves. The physical meaning of each term of the analytical solution can be distinguished, which is beneficial for exploring the flux exchange at the sediment water interface in mobile beds.
简介 Brief introduction
借助理论推导和解析解的方式分析了水沙运动对于水沙界面处营养盐通量的影响。构建了不同模式下底泥营养盐通量的统一表达式,重点考虑沙波运动的影响,并将其引入描述营养盐输移和交换的偏微分方程组,求解得到解析表达式,进而可以计算上覆水和底泥中的营养盐浓度以及底泥通量的时空变化规律。在此基础上进一步分析了沙波参数、水深和泥沙粒径对于底泥通量的影响,确定了控制底泥通量大小的关键参数。
扫码关注立方体公众号,实时追踪课题组最新科研进展



