题目 Title
A hierarchical clustering method of hydrogen bond networks in liquid water undergoing shear flow.
期刊 Journal
Scientific Reports (IF=4.38)
作者 Author
Gao, YT; Fang, HW; Ni, K
摘要 Abstract
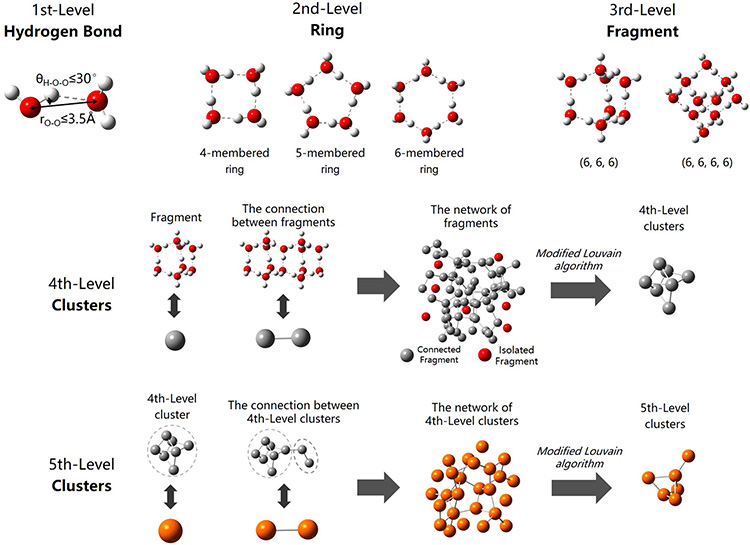
Many properties of water, such as turbulent flow, are closely related to water clusters, whereas how water clusters form and transform in bulk water remains unclear. A hierarchical clustering method is introduced to search out water clusters in hydrogen bonded network based on modified Louvain algorithm of graph community. Hydrogen bonds, rings and fragments are considered as 1st-, 2nd-, and 3rd-level structures, respectively. The distribution, dynamics and structural characteristics of 4th- and 5th-level clusters undergoing non-shear- and shear-driven flow are also analyzed at various temperatures. At low temperatures, nearly 50% of water molecules are included in clusters. Over 60% of clusters remain unchanged between neighboring configurations. Obvious collective translational motion of clusters is observed. The topological difference for clusters is elucidated between the inner layer, which favors 6-membered rings, and the external surface layer, which contains more 5-membered rings. Temperature and shearing can not only accelerate the transformation or destruction of clusters at all levels but also change cluster structures. The assembly of large clusters can be used to discretize continuous liquid water to elucidate the properties of liquid water.
简介 Brief introduction
本文基于分子动力学模拟液态水,根据液态水的氢键网络提出一种基于图论的分层式团簇搜索方法,将液态水的微观结构分为氢键、环、片元及团簇等若干层次结构,提出一种水的微观结构的理解,并且对比有无剪切的情况下水的微观结构变化,发现温度和剪切作用均能促使水分子团簇的破碎。
扫码关注立方体公众号,实时追踪课题组最新科研进展



